While Azure and AWS both offer a suite of security features, understanding the subtle differences in their approaches is crucial for aligning your cloud strategy with your specific business goals.
To help you make an informed decision, we’ve crafted a comprehensive comparison of AWS and Azure security so you can select a cloud provider that seamlessly integrates with your unique needs.
Actionable AWS Security Best Practices [Cheat Sheet]
This cheat sheet goes beyond the essential AWS security best practices and offers actionable step-by-step implementations, relevant code snippets, and industry- leading recommendations to fortify your AWS security posture.
Download nowIs AWS or Azure more secure?
AWS and Azure are the top cloud providers on the market since both Amazon and Microsoft provide extensive cloud platforms. Because these providers both offer quality security features, your decision mainly depends on the infrastructure you already use, your organization’s needs, and how you plan on managing your cloud environment.
Whether you want the most flexible options for integration with your existing tools or more granularity and security controls, it’s essential to pick the right fit for your organization based on key categories. Below, you’ll find a snapshot of what security types AWS and Azure work best for:
| Security domain | Winner |
|---|---|
| Identity and access management | Azure |
| Logging and monitoring | Tie |
| Compliance | Tie |
| Threat detection | Azure |
| Security posture management | Azure |
| Key management and encryption | Tie |
| Network security | AWS |
Now, let’s dig into each security type:
1.Identity and access management
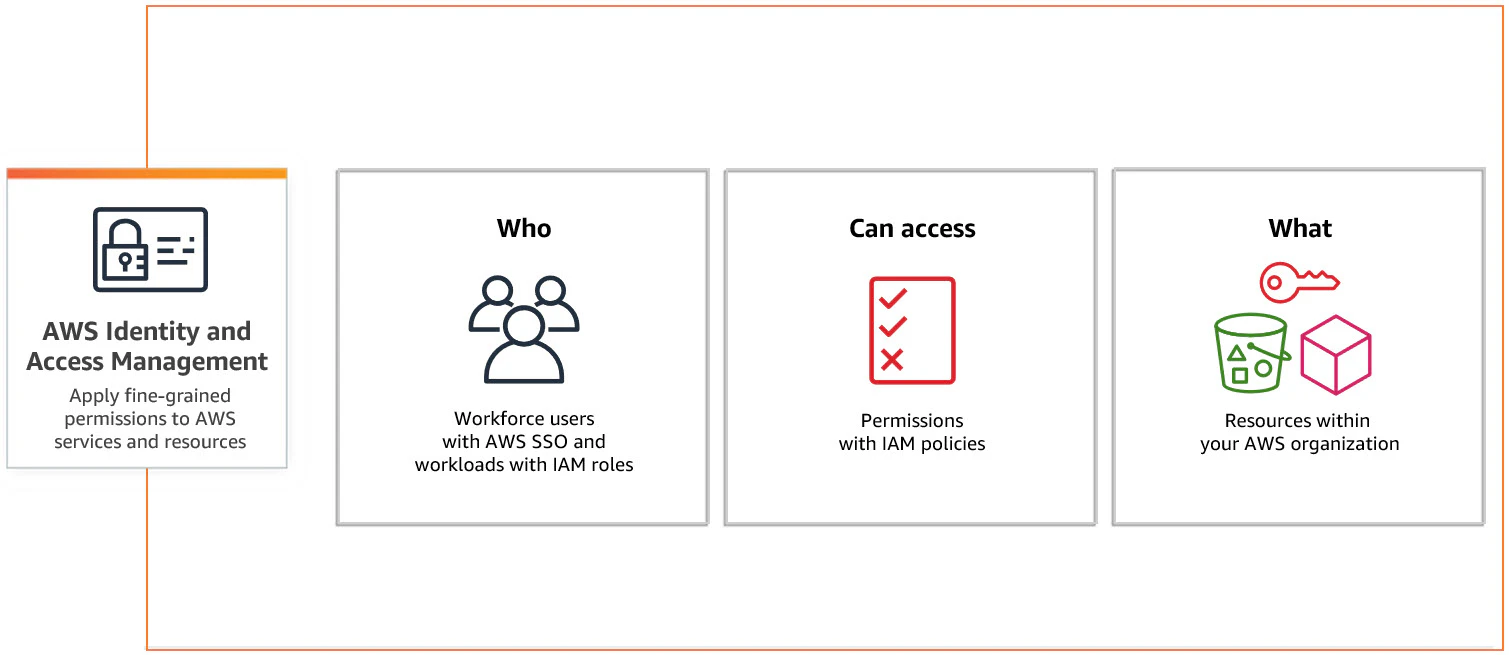
Identity and access management (IAM) ensures that only authorized individuals or systems have access to resources within a cloud environment and that those authorized parties can access only what they need.
AWS and Azure both offer cloud-based IAM solutions that your organization can configure to meet its requirements.
AWS IAM
AWS IAM roles define which actions identities that you assign to specific roles can perform. Users, groups, applications, or services can assume roles, and you can create AWS IAM policies to specify allowed actions on particular AWS resources. These policies, written in JSON, attach to users, groups, or roles for fine-grained access.
Key features and capabilities:
Identity federation: Integrates with on-premises identity systems that use open standards like SAML 2.0, OAuth 2.0, and OpenID Connect
Seamless integration: Works with AWS IAM or AWS IAM Identity Center for unified authentication across cloud and on-premises environments
Advanced access control: Supports attribute-based access control for more dynamic, context-aware security policies
Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Enhances security with an extra authentication layer
Log and service integration: Provides log monitoring, security event tracking, and built-in AWS service compatibility for streamlined security management
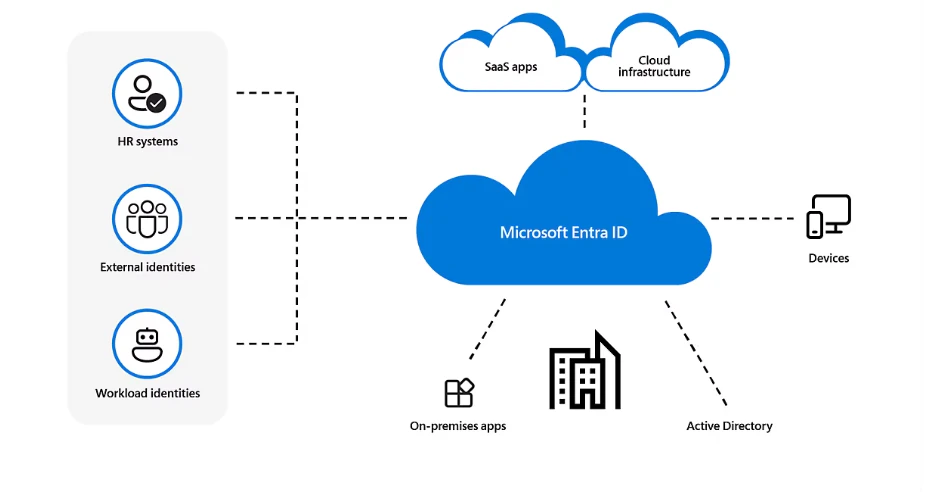
Microsoft Entra ID
Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) is Azure’s cloud IAM solution. To manage access to Azure resources, you can leverage role-based access control (RBAC) with identities you’ve created in Microsoft Entra ID.
RBAC defines roles with fine-grained permissions, the scope of application, and the security principles you’ve assigned to each role. Security principals could be users, groups, or identities associated with an application. You can use predefined Azure roles (such as owner or contributor) or create your own custom roles.
Key features and capabilities:
First-party identity ecosystem: Integrates with Microsoft Active Directory using Microsoft Entra Connect for identity synchronization
Broad identity support: Supports SAML, OpenID Connect, and OAuth 2.0 for compatibility with various identity management systems
Custom identity provider integration: Enables custom connectors for third-party identity providers through Azure AD B2C
Enterprise-grade security: Offers MFA, single sign-on, conditional access, and privileged identity management for enhanced protection
Seamless service integration: Provides built-in IAM integration with Azure services for streamlined identity management
Winner
Azure’s Microsoft Entra ID wins. This tool is effective for organizations that use Active Directory since it integrates seamlessly.
AWS, however, does offer more flexibility for managing complex, multi-cloud environments with fine-grained access controls like ABAC, SCPS, and STS.
2. Logging and monitoring
Both AWS and Azure provide comprehensive logging and monitoring capabilities to give customers insights into hosted workloads’ status and health. Let’s look at how they stack up:
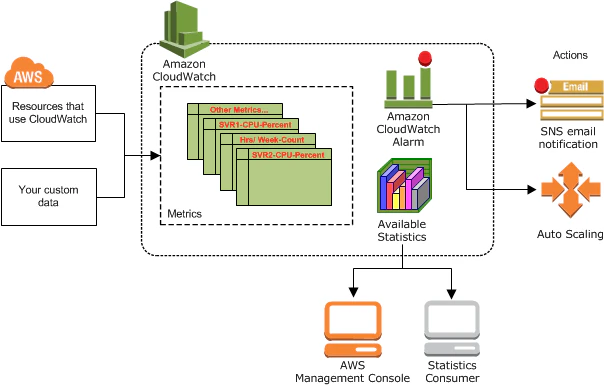
AWS CloudWatch Logs
AWS provides comprehensive log analytics capabilities through AWS CloudWatch Logs, which allows you to stage and query the logs it collects from various AWS resources. (One thing to note: the querying capability can be quite limited and might require integration with additional tools like AWS Elasticsearch for advanced analytics.)
Key features and capabilities:
Audit logging: AWS CloudTrail records an audit trail of API calls to AWS resources for visibility and compliance.
Application diagnostics: AWS X-Ray traces and collects performance data from AWS-hosted applications.
Resource monitoring: Amazon CloudWatch consolidates and provides metrics from various AWS resources.
Network traffic analysis: Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Flow Logs offer visibility into traffic flow between Amazon VPCs for security and performance monitoring.
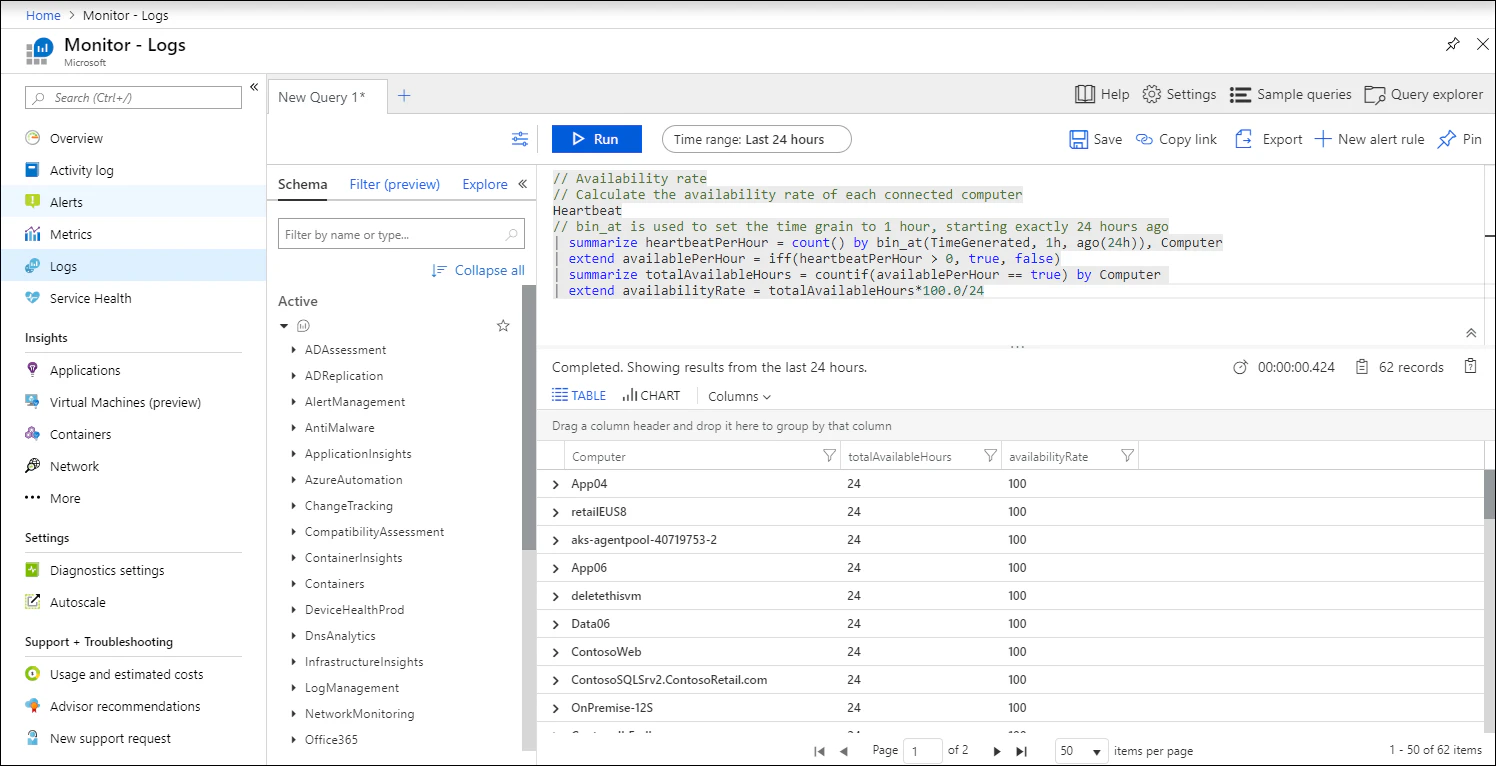
Azure Monitor Logs
Azure leverages Azure Monitor Logs as a central hub for log analysis. With it, you can run robust queries and conduct in-depth analyses to gain meaningful insights. Your team can also use Azure to get visibility into activities associated with Azure resources.
Key features and capabilities:
Performance monitoring: Azure Diagnostics collects metrics, logs, and traces for troubleshooting and system insights.
Application insights: Azure Application Insights provides deep performance analytics, usage monitoring, and debugging reports.
Centralized monitoring: Azure Monitor aggregates and tracks metrics across Azure, as well as multi-cloud and hybrid environments.
Network diagnostics: Azure Network Watcher offers built-in network monitoring, traffic analysis, and visualization for Azure Virtual Networks (VNets).
Winner
It’s a tie. Security teams find AWS CloudWatch Logs easier to set up, especially due to its integrations with SDKs and APIs. At the same time, Azure Monitor Logs offers more complex querying through its Kusto Query Language.
3. Compliance
Each organization manages compliance processes differently due to factors like its industry, geographic location, and level of data sensitivity. While both AWS and Azure offer comprehensive compliance management capabilities, choosing between them depends on your organization’s specific needs and requirements.
AWS’s compliance capabilities
You can use AWS Organizations, along with AWS IAM, to manage and segregate multiple accounts. For example, AWS Control Tower is a service you can use to design an AWS environment that aligns with compliance best practices.
Key features and capabilities:
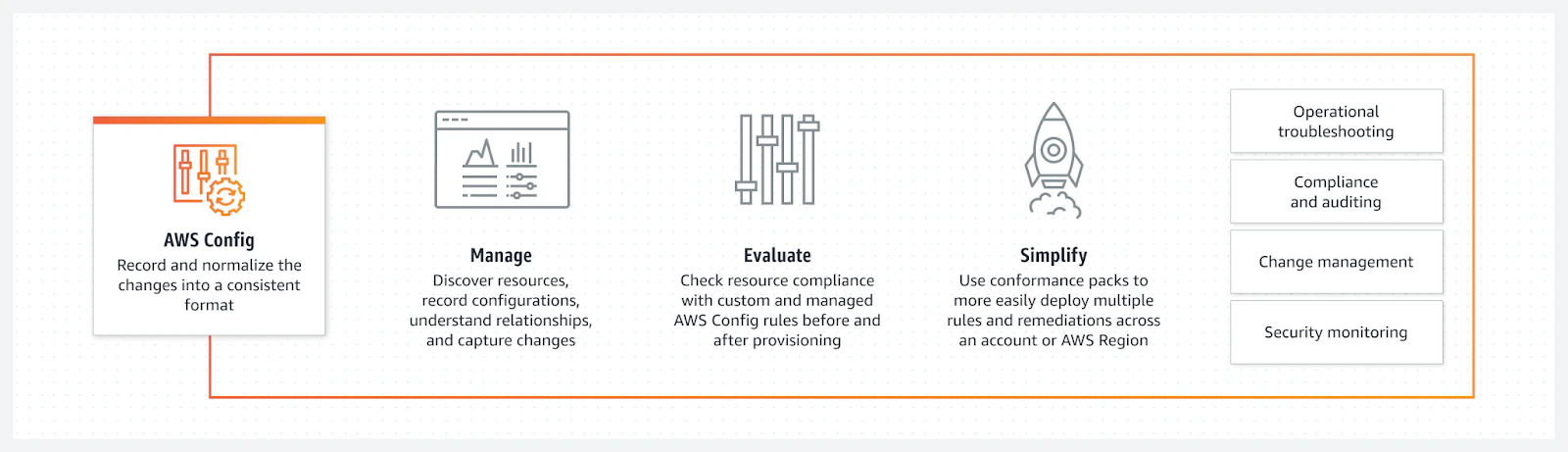
Continuous compliance monitoring: AWS Config assesses, audits, and evaluates AWS configurations to maintain compliance.
Best-practice recommendations: AWS Trusted Advisor provides suggestions for resource optimization and security improvement.
Regulatory compliance support: AWS Artifact offers access to compliance reports and certifications for GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and more.
Azure’s compliance capabilities
To enforce compliance policies in Azure, Azure Policy helps you implement predefined and customizable restrictions. Azure Blueprints also lets you create reusable governance artifacts. You can use these services with a resource hierarchy through Azure management groups, subscriptions, resource groups, and resources.
Key features and capabilities:
Continuous compliance assessment: Azure Policy enforces rules and configurations to maintain compliance with industry standards.
Security and compliance monitoring: Microsoft Defender for Cloud detects and flags non-compliant resources in real time.
Regulatory compliance support: Azure Trust Center provides access to audit reports and certifications for leading compliance standards.
Winner
It’s a tie. Both AWS and Azure have extensive compliance frameworks, like AWS Artifact and Azure Trust Center. Both platforms also offer continuous enforcement and compliance assessment with tools like AWS Config, AWS Control Tower, Azure Policy, and Microsoft Defender.
4. Threat detection
The choice of threat detection services in AWS and Azure depends on many factors, such as integrations with existing services and specific threat detection and reporting requirements. Additionally, you should first evaluate the remediation capabilities that your organization requires.
Threat detection in AWS
AWS Config identifies non-compliant configurations that threat actors could exploit. (Still, you should also follow the recommendations from AWS Trusted Advisor to eliminate security loopholes.)
For dynamic protection from threats, you can use services like Amazon GuardDuty—which leverages machine learning to analyze inputs from various sources, including VPC Flow Logs, DNS logs, and CloudTrail events—to detect potential threats.
Key features and capabilities:
Compliance auditing: Use AWS Config to verify that your policies, resources, and infrastructure meet governing requirements.
Catch changes from unauthorized instances: Find unauthorized actions within your configurations.
Continuous monitoring: Track configurations across your AWS resources in real time.
Threat detection in Azure
Microsoft Defender for Cloud offers static threat detection by evaluating resources to prevent misconfigurations while providing recommendations to remediate them. It can also provide real-time dynamic threat detection by analyzing data from various Azure resources, applications, and network traffic. You can manually configure remediation in Microsoft Defender for Cloud or automate it using Azure Logic Apps.
While Azure offers integrations with third-party security services and tools for threat detection and reporting, one of its biggest strengths is its integration with existing Microsoft security solutions.
Key features and capabilities:
Automated detection: You can use Azure for machine learning, which automatically finds anomalies so you can proactively prevent threats.
Intelligent reporting: Azure’s threat protection provides analyses using Microsoft Defender for Cloud and Microsoft Sentinel, which can spot abnormal behavior in users and your cloud environment and help you find new threats.
Detection tuning: Microsoft continuously uses algorithms to analyze customer data and consistently works with security researchers to improve its overall security.
Winner
Azure’s threat detection wins. Due to its more advanced threat detection capabilities, Azure offers a competitive advantage over AWS. However, AWS GuardDuty is also great for automatic threat detection using machine learning.
5. Security posture management
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) is a set of tools, processes, and practices that help you maintain and manage your security posture across cloud infrastructure, apps, and data.
Let’s look more closely at AWS Security Hub vs. Microsoft Defender for Cloud (formerly Azure Security Center):
AWS Security Hub
AWS Security Hub provides cloud security posture management by checking the status of security best practices, identifying misconfigurations, creating alerts, and carrying out automated security threat remediation across AWS accounts and regions. It can also check your services’ configuration against industry-standard security benchmarks, such as CIS and PCI.
Key features and capabilities:
Hybrid security integration: Provides limited support for on-premises and multi-cloud environments in AWS Security Hub
Third-party security integration: Consolidates findings from external security tools to create a unified security view
Context-aware threat response: Enhances security findings with additional context to improve risk assessments
Automated remediation: Leverages Amazon EventBridge to trigger automatic responses to flagged security events
Centralized security dashboard: Offers a single view of security insights from multiple sources for streamlined monitoring and reporting
Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is Azure’s cloud security posture management service. In addition to providing visibility into the status of your security posture and flagging misconfigurations, it also includes hardening guidance.
While some of these foundational features are free, Microsoft also offers capabilities for compliance management, attack path analysis, and advanced threat hunting in a Defender CSPM pricing tier.
Key features and capabilities:
Cross-cloud security: Protects resources across Azure, AWS, GCP, and on-premises environments with Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Regulatory compliance benchmarking: Performs compliance checks for AWS, GCP, and Azure using industry security standards
Centralized security dashboard: Delivers visibility into security and compliance statuses across multiple environments
Automated remediation: Leverages Azure Logic Apps to streamline and automate security response workflows
Winner
Azure’s Microsoft Defender for Cloud wins. While AWS Security Hub may be limited as a CSPM platform, Azure’s Defender for Cloud provides multi-cloud security for a flexible choice, especially for hybrid cloud environments. It also supports AWS workloads.
6. Key management and encryption
Key management and encryption secure sensitive data and protect cloud-stored information’s confidentiality and integrity.
AWS Key Management Service
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) lets you create encryption keys and manage their lifecycle. KMS also enables server-side encryption for various AWS services, including AWS RDS, Amazon EBS, and Amazon S3. You can leverage AWS KMS with AWS Encryption SDK to enable client-side encryption.
Key features and capabilities:
Seamless AWS integration: Natively integrates with AWS services to streamline encryption management
Key usage monitoring: Tracks and audits encryption key activity through AWS CloudTrail
Automatic key rotation: Enables auto-rotation for AWS-managed keys and optional rotation for customer-managed keys
Azure Key Vault
Azure’s native key management service, Azure Key Vault, allows you to create, manage, and store cryptographic keys and secrets at scale.
Key features and capabilities:
Comprehensive encryption: Supports server-side encryption for Azure Storage, Managed Disks, and SQL Database, plus client-side encryption
Seamless Azure integration: Works out of the box with Azure services, including Azure Monitor, for logging and auditing key access
Automated key rotation: Enables policy-based key rotation for better control over the encryption key lifecycle
Winner
It’s a tie. Both Azure and AWS support automatic key rotation, auditing, and integration with cloud-native services.
7. Network security
Making informed cloud security decisions relies on a clear understanding of AWS and Azure network security services. Let’s dive in:
AWS’s network security
AWS uses VPC for network segregation. To isolate cloud resources, it offers features like subnets, route tables, security groups, and network access control lists, which control the network traffic flow between different components.
Key features and capabilities:
Secure service access: AWS PrivateLink enables private connectivity to AWS services without Internet exposure.
Web application protection: AWS WAF defends applications against common exploits and attacks.
DDoS mitigation: AWS Shield provides managed volumetric and application-layer distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) protection.
Azure’s network security
Azure VNet is the logical network construct that offers network segregation in Azure, with features such as subnets, route tables, and network security groups (NSGs). Together, NSGs and Azure Firewall control inbound and outbound traffic for Azure resources.
Key features and capabilities:
Network traffic control: NSGs function as a distributed firewall at the network interface and subnet levels.
Secure service access: Azure VNet services endpoints, and Azure Private Link enables private connectivity to Azure services.
DDoS mitigation: Azure DDoS Protection safeguards applications from DDoS attacks with tiered protection plans.
Winner
AWS’s network security wins. While both platforms offer arguably equal value, AWS VPC’s fine-grained control over network policies and its additional tools provide advanced, customizable network security with strong DDoS protection. Azure does, however, offer a strong firewall and DDoS protection.
Who’s the winner overall?
Most of the results are tied. Your ideal infrastructure for security depends on how you’ve built your cloud environment, whether with Azure tools or AWS tools. Still, Azure wins primarily in the security category for more holistic and flexible features.
Either way, cloud security doesn’t stop with AWS and Azure. You still need to implement the highest-quality tools, best practices, and management to protect your data—and you can start by picking a cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP).
The Cloud Security Workflow Handbook
A practical guide to transforming security teams, processes, and tools to support cloud development.
Download nowEnhancing cloud-native security with Wiz
Native security tools provide a strong foundation for your cloud environment. However, it's essential to improve them with specialized security tools tailored to your organization, especially in multi-cloud environments.
Wiz offers comprehensive cloud security through a portfolio of enterprise-class services, which includes CSPM, vulnerability management, data security posture management, and cloud infrastructure entitlement management. Its CNAPP also offers 100% visibility into workloads among different clouds through its graph-based, agentless solution, which leads the industry in prioritizing and resolving security issues.
With Wiz’s real-time threat detection and end-to-end visibility, you can track and eliminate attack vectors, which can help you augment Azure and AWS’s native capabilities for greater cloud security.
Download Wiz’s Azure Security Best Practices [Cheat Sheet] today for more information on leveraging Azure and Wiz for top-of-the-line security.
Complete Cloud Visibility, Regardless of your Environment
Learn why CISOs at the fastest growing organizations choose Wiz to help secure their AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud environments.